The “hottest day” is not that hot, and very irrelevant
So the news cycle went hyperbolic over a single dubious hot day in records that only go back 0.01% of human existence. Remember when “30 year trends” were all that mattered?
Let’s ignore for the moment that the error bars on measurements of global temperature in 1899 would make any normal scientist blush. Who believes for one minute even today we can measure the global surface temperature to one hundredth of a degree? The cringeworthy insignificant digits were everywhere. On Monday the Earths surface was supposedly 17.01 degrees Celsius for the first time in “human history”. Then Tuesday it was 17.18C, Hallelujah. Who are we kidding?
Probably the biggest lie was to call this “human history” as if the ancient Egyptians were measuring the temperature on Earth and every day of the week. Are we really sure we know what the temperature was on July 3, 2201 BC? Maybe it was 17.31C that day — prove me wrong? We have no idea how hot the “hottest days” were for 99% of human civilization. The best proxies we have can’t tell us what the temperature was for 24 hour periods. We can’t compare 20 year smoothed averages with a single 24 hour snapshot. Well, scientific prostitutes can, but not real scientists.
If it was a record “hottest day”, it might have been the hottest day in the last 40 years (maybe, and if only we had good thermometers, didn’t put them at airports, near air conditioners and incinerators, didn’t go electronic, hide the calibration data, and adjustify the records, eh?). It’s a big so-what.
And in the end we know it there have been hotter years before in human civilization, and probably thousands of them.
Who is trying to erase the Holocene?
Don’t they teach climate scientists anything anymore? Karsten Haustein, from the University of Leipzig was telling the BBC that July will possibly be the hottest “since the Eemian”, 120,000 years ago, as if the Holocene optimum period didn’t exist.
A mere 5,000 years ago sea levels were higher, corals were happy, people thrived, and Greenland was a lot warmer. This was a global phenomenon — higher sea levels and some 6,000 boreholes drilled around the world show the same pattern.
It was hotter for thousands of years and CO2 was irrelevant. What the world needs are some real science journalists who can ask these badly trained junior modelers what happened to the Holocene?

This graph shows the ice-core data up until 1855. The last 150 years (1705 to 1855) are highlighted in red to show the warming as the Earth began coming out of the Little Ice Age.
Sea levels were higher all around the world
How could the oceans be higher all around the world if the world was not warmer? Sea levels have been falling for the last 7,000 years around Australia, they used to be nearly 1m higher in the South China Sea, South Africa and Polynesia and it’s a similar pattern around the world (thanks NoTricksZone). Studies on mangroves in Brazil show sea levels were about 2.7 meters higher in the mid-Holocene, and mangroves grew 34 kilometers further inland. (Fontes et al 2017). CO2 Science lists references all over the world. I am barely skimming the surface.
Other researchers estimate the waters flowing out of the Pacific Ocean past Indonesia were a full 2 degrees Celcius warmer 7,000 years ago. (Rosenthal, (2013). Somehow corals did not go extinct, ancient viruses didn’t wipe out the Sumerians, and humans spread across the Earth.
Sea levels were higher off the very geologically stable Western Australia 7,000 years ago. Across the other side of Australia in NSW sea levels were 1 – 1.5m higher.
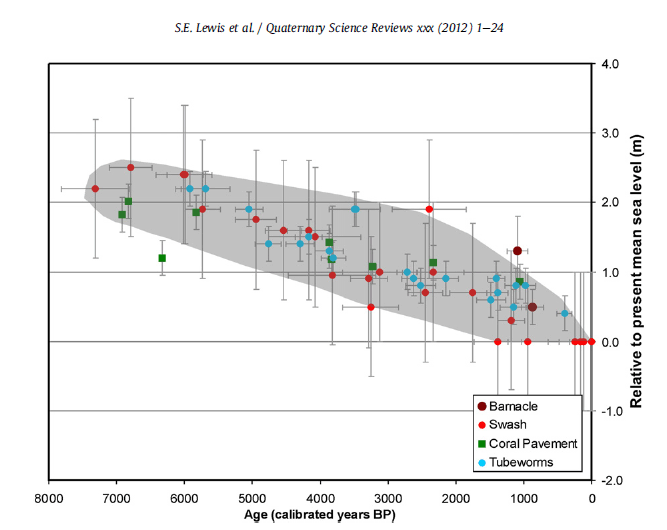
Sea level has been falling for 7,000 years in Western Australia (Lewis et al)
A thousand stories of human pain and triumph from the last ten thousand years are being erased from the records. Australian Aboriginals apparently struggled through a 1,500 year mega drought about 6,000 years ago (see McGowan et al 2012). And massive fires raged across far north Australia 4,000 years ago that were far worse than today. (Rehn et al 2021).
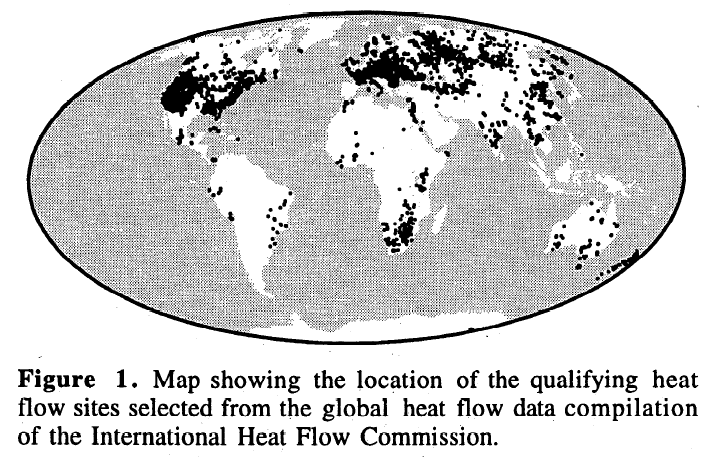
Another proxy suggesting the Holocene warmer temperatures were global is the heat flow data measured in 6,000 boreholes across six continents down to about 2km. Sometime from 5,000 to 10,000 years ago temperatures were hotter than they are now.
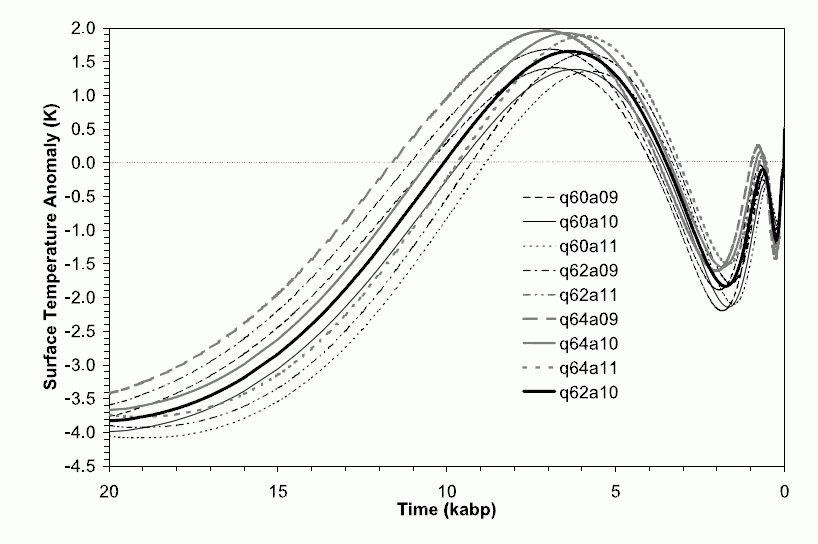
6,000 boreholes drilled around Earth show temperatures were hotter in the holocene. Figure 1. Suite of reconstructions of surface temperature history over the last 20,000 years. Nine curves correspond to three values of thermal diffusivity. The reference level is the mean of the instrumental record from 1961-1990 AD. (Huang et al 2008)
The hottest day in the last 150 years is irrelevant.
REFERENCES
Fontes et al (2017) The Impacts of the Middle Holocene High Sea-Level Stand and Climatic Changes on Mangroves of the Jucuruçu River, Southern Bahia – Northeastern Brazil, Radiocarbon , Volume 59 , Issue 1 , February 2017 , pp. 215 – 230. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/RDC.2017.6
Huang, S. P., H. N. Pollack, and P.-Y. Shen (2008), A late Quaternary climate reconstruction based on borehole heat flux data, borehole temperature data, and the instrumental record, Geophys. Res. Lett., 35, L13703, doi:10.1029/2008GL034187 [PDF] Long blog discussion on boreholes.
Lewis, S.E., et al., Post-glacial sea-level changes around the Australian margin: a review, Quaternary Science Reviews (2012), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.09.006 [abstract]
Hamish McGowan,Samuel Marx, Patrick Moss, Andrew Hammond (2012): Evidence of ENSO mega-drought triggered collapse of prehistory Aboriginal society in northwest Australia, Geophysical Research Letters, Vol 39, Issue 22. DOI: 10.1029/2012GL053916 [Abstract]
Rehn, E. et al (2021) A late-Holocene multiproxy fire record from a tropical savanna, eastern Arnhem Land, Northern Territory, Australia [PDF]
Rosenthal, Y., Braddock K. Linsley, Delia W. Oppo (2013) Pacific Ocean Heat Content During the Past 10,000 Years, Science 1 November,Vol. 342 no. 6158 pp. 617-621 DOI: 10.1126/science.1240837 [Sciencemag.org ]